By Raquel Jones, Intern, and Marianne Eppig, Manager of Research & Communications
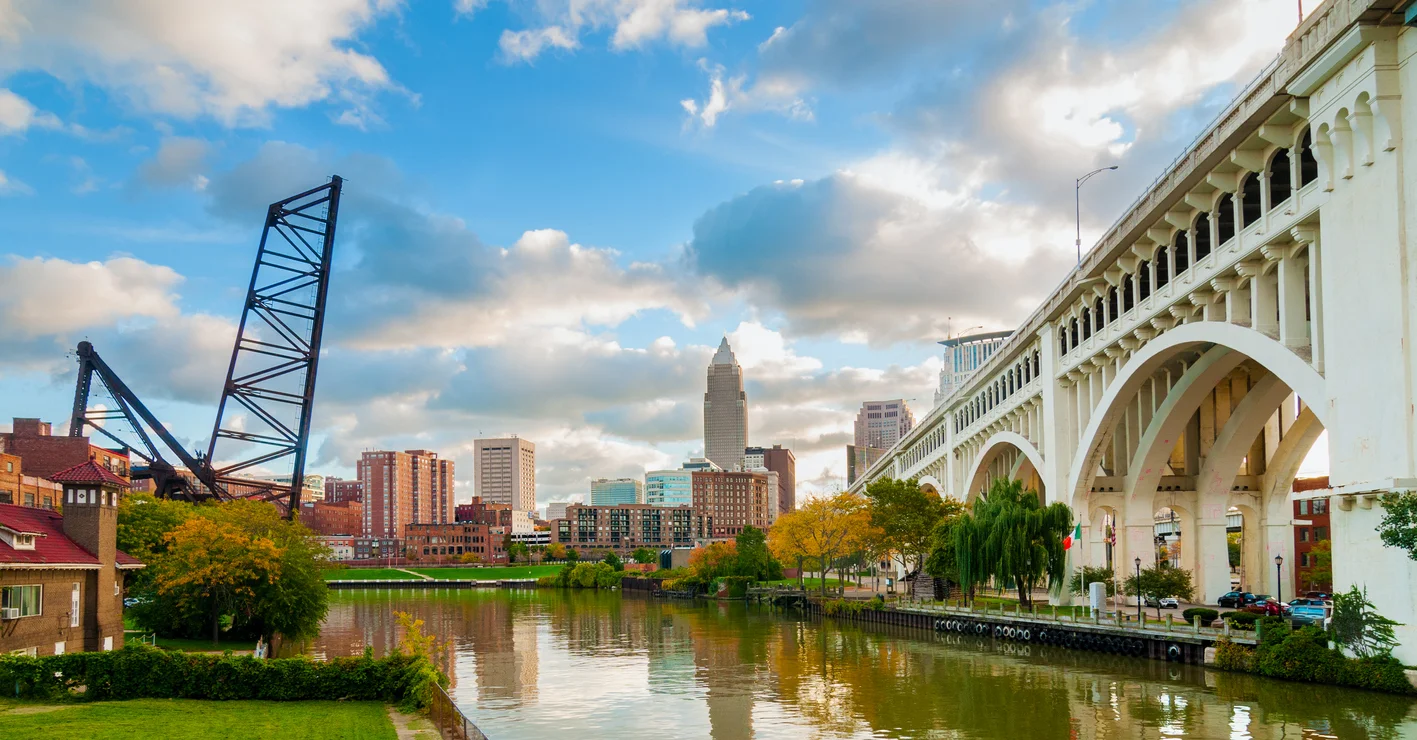
Between the years 1970 and 2013, the city of Cleveland lost almost half of its population. In fact, most cities in the region have also witnessed a decline in population. However, this recent trend seems to have less to do with the location and more to do with the layout of these cities. The most evident reason for this rapid decline may point to the fact that young, educated Millennials favor core cities, as opposed to sprawling communities.
According to research conducted by the Pew Institute and Urban Land Institute, Millennials are driving less than previous generations. However, the Millennials are not alone in this recent trend, as the Baby Boomers are also eager to take advantage of urban amenities and walkable communities. A key component to attracting Millennials to cities is the availability and quality of transportation options. According to a recent survey, “55% of Millennials have a preference to live close to transit” (Yung). With more than half of those polled in favor of such an option, it is obvious that the demand for a multimodal city is real.
One of the most compelling arguments supporting this growing rejection of a car-dependent society points heavily at the financial strain induced by the costly upkeep of a car. With gas prices rising and car loans becoming harder to obtain, and as Millennials find themselves buried in a heap of college debt, owning a car no longer seems to be practical. For this reason, many are shifting to urban areas, where there are multiple transportation options and where almost everything that could be wanted or needed is only a short distance away.
For the graphs above, Millennials were defined as being born between 1981 and 2000.
In Ohio, we need to do more to take advantage of these trends and to continue attracting and retaining populations that are interested in urban living in order to strengthen the economies of these cities and their surrounding regions. Some of Ohio's cities are seeing more positive trends--attracting a greater percentage of Millennials--but in the context of ongoing population shrinkage in all of our major cities except Columbus, it is clear that Ohio's work is not done. The state’s ability to leverage market demand for inner city living and further incentivize—and remove legislative barriers to—infill development within its cities will help determine Ohio’s future prosperity.
For more information about these national demographic trends, take a look at these articles:
- "Demographic Preferences Shifting in Favor of Walkable, Urban Communities" by John Yung (Note: these trends were the focus of the American Planning Association's 2014 National Planning Conference)
- "What Millennials Want: A Multi-Modal City" by James Brasuell